Frequently Asked Questions
I Have A Bug, Help!?
Nice work, now create an issue report here with details on what caused the crash. Uploading a zip of your code and/or a minimal reproducible example is very appreciated, and will make bug fixes faster.
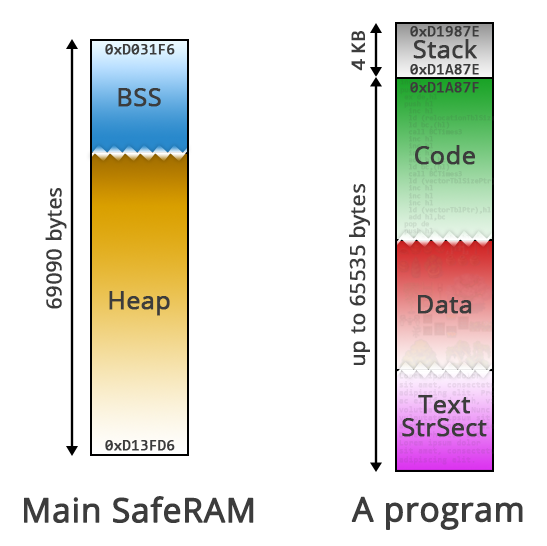
What is the C Runtime Memory Layout?
The CE has a limited amount of memory. The stack is roughly 4KiB bytes in size, while the bss/heap grow into each other and consume roughly 64KiB. The following graphic breaks down the address space.
Linking Assembly Source Files
Assembly routines can be linked into a C program provided the following conditions are met:
The file’s extension is .asm. It can be placed at any depth in the sources directory.
The routine should have a C prototype if it used externally in C.
The assembly routine must be prefixed with an underscore, and have a corresponding public entry in the assembly file.
Any external functions called from the assembly source must be listed as being extern.
Below is an example assembly source file that relies on an external function:
public _asm_func
_asm_func:
pop hl
pop de
push de
push hl
call _external_func
ret
extern _external_func
The C prototype is shown below:
C File:
void asm_func(int a);
Arguments and Returns
Arguments are pushed from last to first corresponding to the C prototype. In eZ80, 3 bytes are always pushed to the stack regardless of the actual size. However, the assembly function must be careful to only use the valid bytes that are pushed. For example, if a short type is used, the upper byte of the value pushed on the stack will contain arbitrary data. This table lists the locations relative to sp from within the called funciton.
C Type |
Size |
Stack Location |
|---|---|---|
char |
1 byte |
sp + [3] |
short |
2 bytes |
sp + [3:4] |
int |
3 bytes |
sp + [3:5] |
long |
4 bytes |
sp + [6]: sp + [3:5] |
float |
4 bytes |
sp + [6]: sp + [3:5] |
double |
4 bytes |
sp + [6]: sp + [3:5] |
pointer |
3 bytes |
sp + [3:5] |
This table lists which registers are used for return values. The type’s sign does not affect the registers used, but may affect the value returned.
Note
C Type |
Register |
Register Contents |
|---|---|---|
char |
A |
xx |
short |
HL |
?? xx xx |
int |
HL |
xx xx xx |
long |
E:HL |
xx: xx xx xx |
float |
E:HL |
xx: xx xx xx |
double |
E:HL |
xx: xx xx xx |
pointer |
HL |
xx xx xx |